-
Research Article
-
Evaluation of Thermal Performance and Industrial Boiler by Carbon-Free Fuel Conversion
산업용 보일러의 무탄소 연료 전환에 따른 열 성능 평가
-
Jonghwan An, Hyeonrok Choi, Won Yang, Changkook Ryu, Seong-il Kim
안종환, 최현록, 양원, 류창국, 김성일
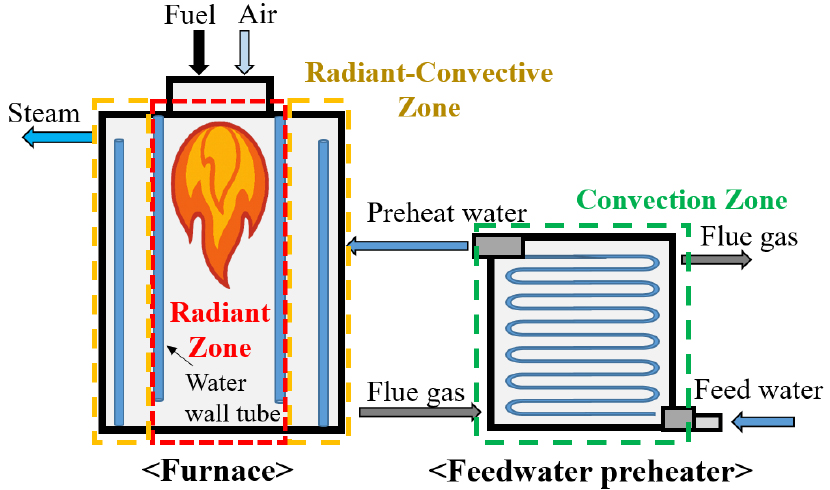
- The conversion of industrial boilers to carbon-free fuels is one of the strategies for reducing carbon emissions. Hydrogen and ammonia, as representative …
- The conversion of industrial boilers to carbon-free fuels is one of the strategies for reducing carbon emissions. Hydrogen and ammonia, as representative carbon-free fuels, emit no CO2 during combustion, and when co-fired with LNG in existing boilers, affect flame temperature, flue gas composition, and flow rate, thereby influencing overall heat transfer characteristics. To evaluate these effects, a process simulation-based model dividing the boiler into radiation and convection zones was developed. The variations in radiative and convective heat transfer characteristics according to variation in the co-firing ratio were quantitatively analyzed, and boiler efficiency was assessed. Variations in flame temperature and flue gas composition affected furnace emissivity and radiative heat transfer, which in turn influenced flue gas temperature, flow rate, and convective heat transfer. As a result of the simulation, hydrogen co-firing increased radiative heat transfer and decreased convective heat transfer, leading to improved boiler efficiency. In contrast, ammonia co-firing decreased radiative heat transfer and increased convective heat transfer, resulting in degraded boiler efficiency. These findings are expected to serve as a basis for the design and operational optimization of industrial boilers utilizing carbon-free fuels. - COLLAPSE
-
Evaluation of Thermal Performance and Industrial Boiler by Carbon-Free Fuel Conversion
-
Research Article
-
Effects of Oxygen Enrichment and Hydrogen Addition on CF4 Decomposition in Methane/Air Counterflow Flames
메탄/공기 대향류 화염에서 산소부화 및 수소 첨가가 CF4 분해에 미치는 영향
-
Ki Yong Lee
이기용
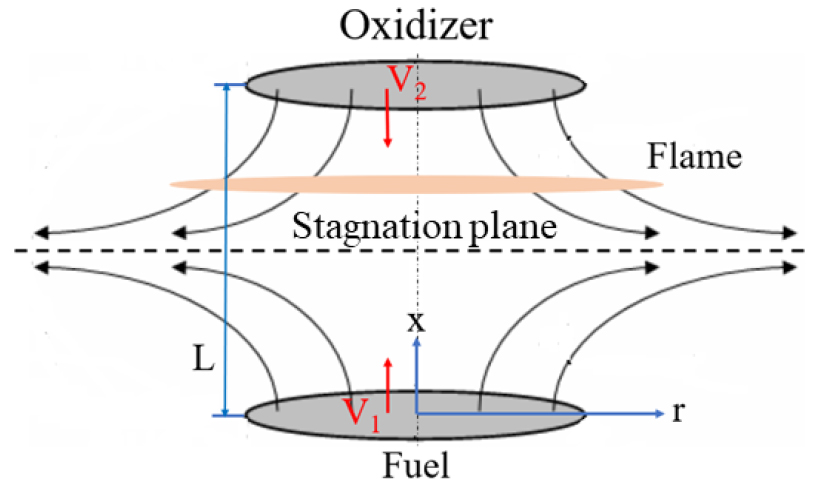
- A numerical analysis is performed to investigate the decomposition rate of CF4 added to the oxidizer side in non-premixed counterflow flames …
- A numerical analysis is performed to investigate the decomposition rate of CF4 added to the oxidizer side in non-premixed counterflow flames of methane with an initial pressure and temperature of 1 atm and 295 K, respectively, under oxygen-enhanced conditions on the oxidizer side or hydrogen added to the fuel side. Furthermore, the changes in axial velocity, maximum flame temperature, and NO concentration are analyzed in flames with a strain rate of 100 s-1. An increase in either the oxygen enrichment rate or the hydrogen addition allows a greater amount of CF4 to be added to the oxidizer without flame quenching, while simultaneously enhancing the CF4 decomposition rate. As the extinguishing condition is approached, the maximum concentration of nitrogen oxide decreases rapidly unlike the maximum flame temperature which decreases linearly. - COLLAPSE
-
Effects of Oxygen Enrichment and Hydrogen Addition on CF4 Decomposition in Methane/Air Counterflow Flames
-
Research Article
-
Analysis of Combustion Instability of Hydrogen Mixed Retrofit Gas Turbine Nozzles
수소혼소 리트로핏 가스터빈 노즐의 연소불안정 특성 분석
-
Juhwan Lee, Sojong Park, Youngbin Yoon, Seung Hyun Yoon, Daesik Kim
이주환, 박소정, 윤영빈, 윤승현, 김대식
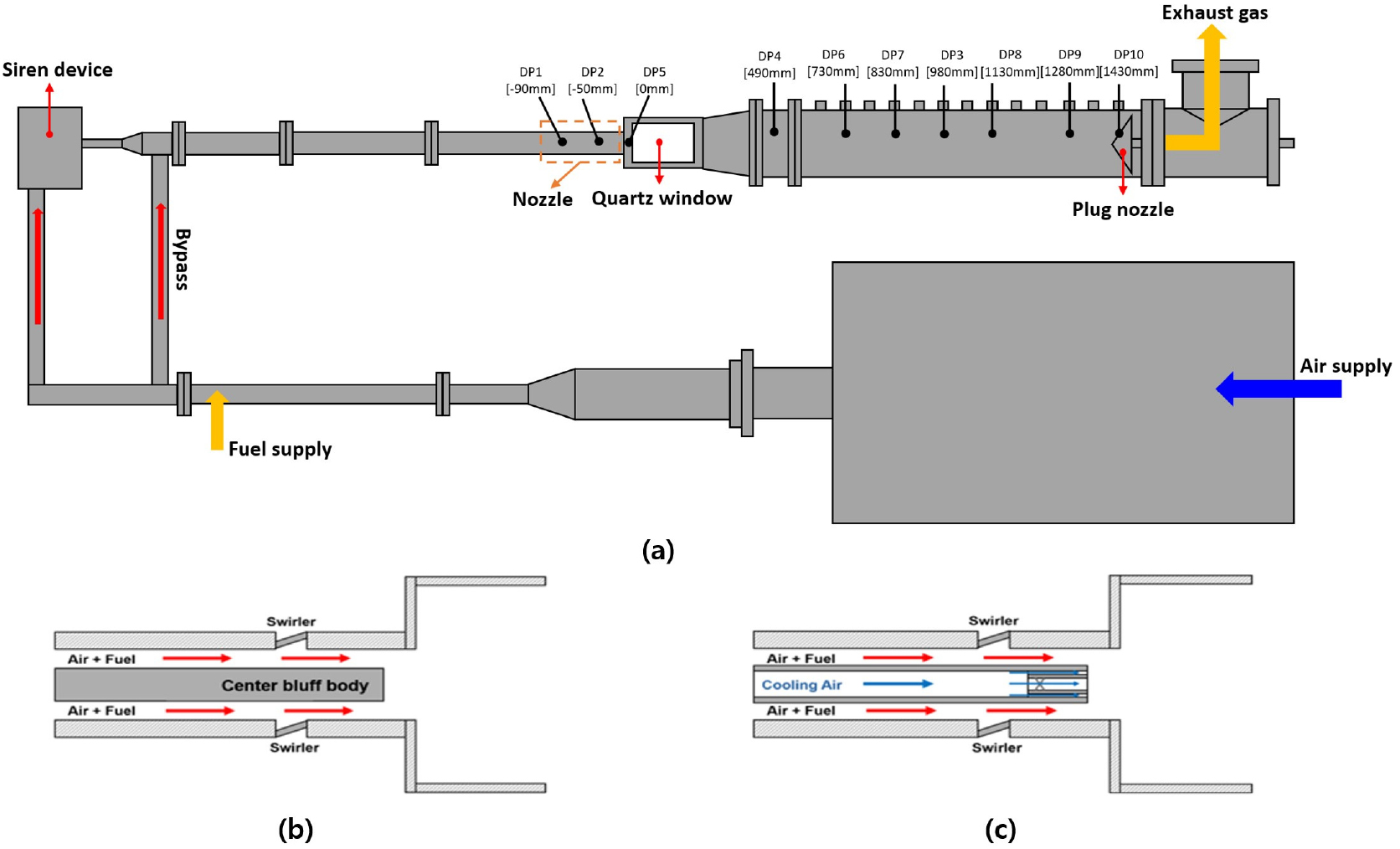
- This study analyzed the combustion instability characteristics of retrofit and original nozzles in hydrogen-mixed gas turbines using a 1D thermoacoustic model. Experiments …
- This study analyzed the combustion instability characteristics of retrofit and original nozzles in hydrogen-mixed gas turbines using a 1D thermoacoustic model. Experiments were conducted on a laboratory-scale test rig at hydrogen mixing ratios of 0%, 30%, and 50%. Both nozzles exhibited frequency shift phenomena with increasing hydrogen content, but showed opposite trends in dynamic pressure amplitude. The original nozzle showed decreased dynamic pressure amplitude with increasing hydrogen ratio, while the retrofit nozzle exhibited increased dynamic pressure amplitude. Analysis of experimentally measured flame transfer functions revealed that the retrofit nozzle exhibited longer time delay than the original nozzle under the same conditions. Root locus analysis confirmed that this difference in time delay is the key factor determining system stability. It was identified that the center cooling air in the retrofit nozzle induces flame lift-off, increasing the time delay. - COLLAPSE
-
Analysis of Combustion Instability of Hydrogen Mixed Retrofit Gas Turbine Nozzles
-
Research Article
-
Study on the Combustion Characteristics of Ethanol Fuel for Various Engine Speed Conditions in a Turbo-Charged SI Engine
Turbo-charged SI기관에서 에탄올 연료의 다양한 엔진회전수 조건에서의 연소 특성에 관한 연구
-
Seung Hyun Yoon, Suhan Park
윤승현, 박수한
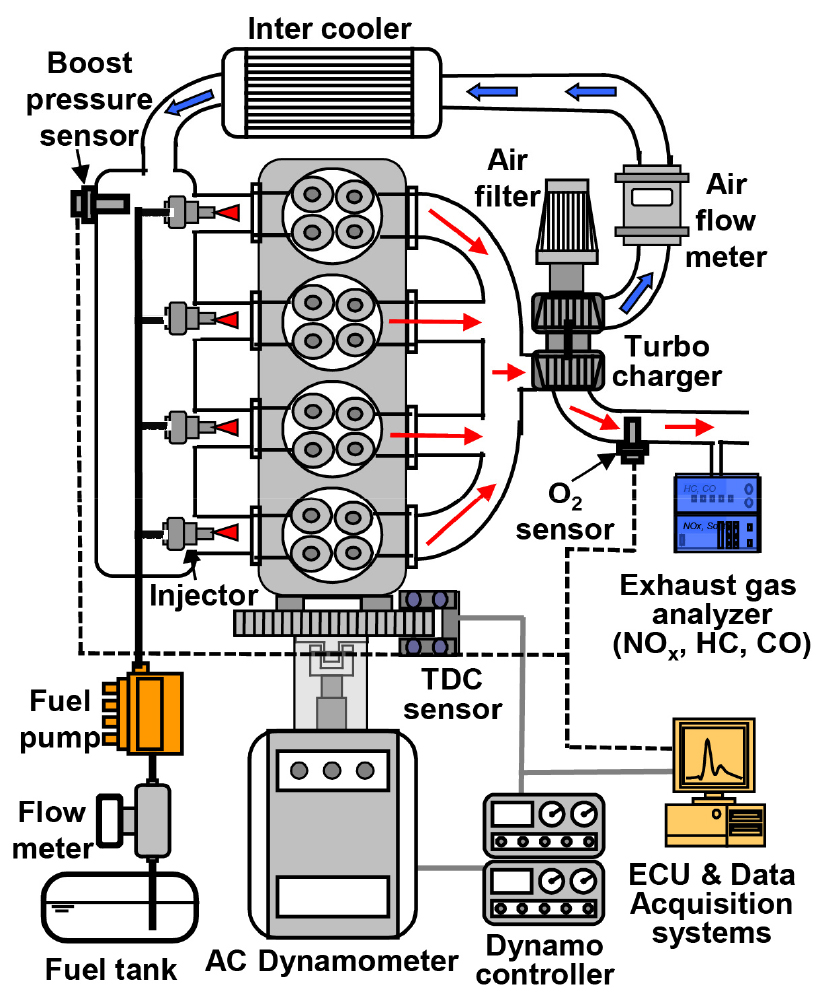
- In this experimental research, the combustion and exhaust emission characteristics of a turbo-charged spark ignition (SI) engine operating on various test fuels …
- In this experimental research, the combustion and exhaust emission characteristics of a turbo-charged spark ignition (SI) engine operating on various test fuels (bioethanol - gasoline blends) were investigated. The study analyzed the key combustion characteristics, including brake torque, exhaust gas temperature, and fuel consumption rate, to determine the influence of the ethanol blends. Furthermore, the reduction effects on exhaust emissions, specifically carbon monoxide, unburned hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides, were compared against those of neat gasoline. The results showed that the brake torque produced by the ethanol-blended fuels was slightly higher than that of neat gasoline. However, brake specific fuel consumption increased with higher ethanol blending ratio due to the lower heating value of ethanol. Overall, ethanol-blended fuels exhibited lower exhaust emissions than neat gasoline across all experimental conditions. The E100 reduced NOx emissions by an average of approximately 10% compared to the G100. - COLLAPSE
-
Study on the Combustion Characteristics of Ethanol Fuel for Various Engine Speed Conditions in a Turbo-Charged SI Engine
-
Research Article
-
A Study of MILD Combustion Characteristics Using FGR in a 180 kWth Incinerator
180 kWth 급 소각로에서 FGR을 이용한 MILD 연소 특성 연구
-
Seonghwan Hwang, Taeyoung Chae, Woohyun Sim, Yongwoon Lee, Won Yang, Jae Wook Lee, Oh Chae Kwon, Minsoo Kim
황성환, 채태영, 심우현, 이용운, 양원, 이재욱, 권오채, 김민수
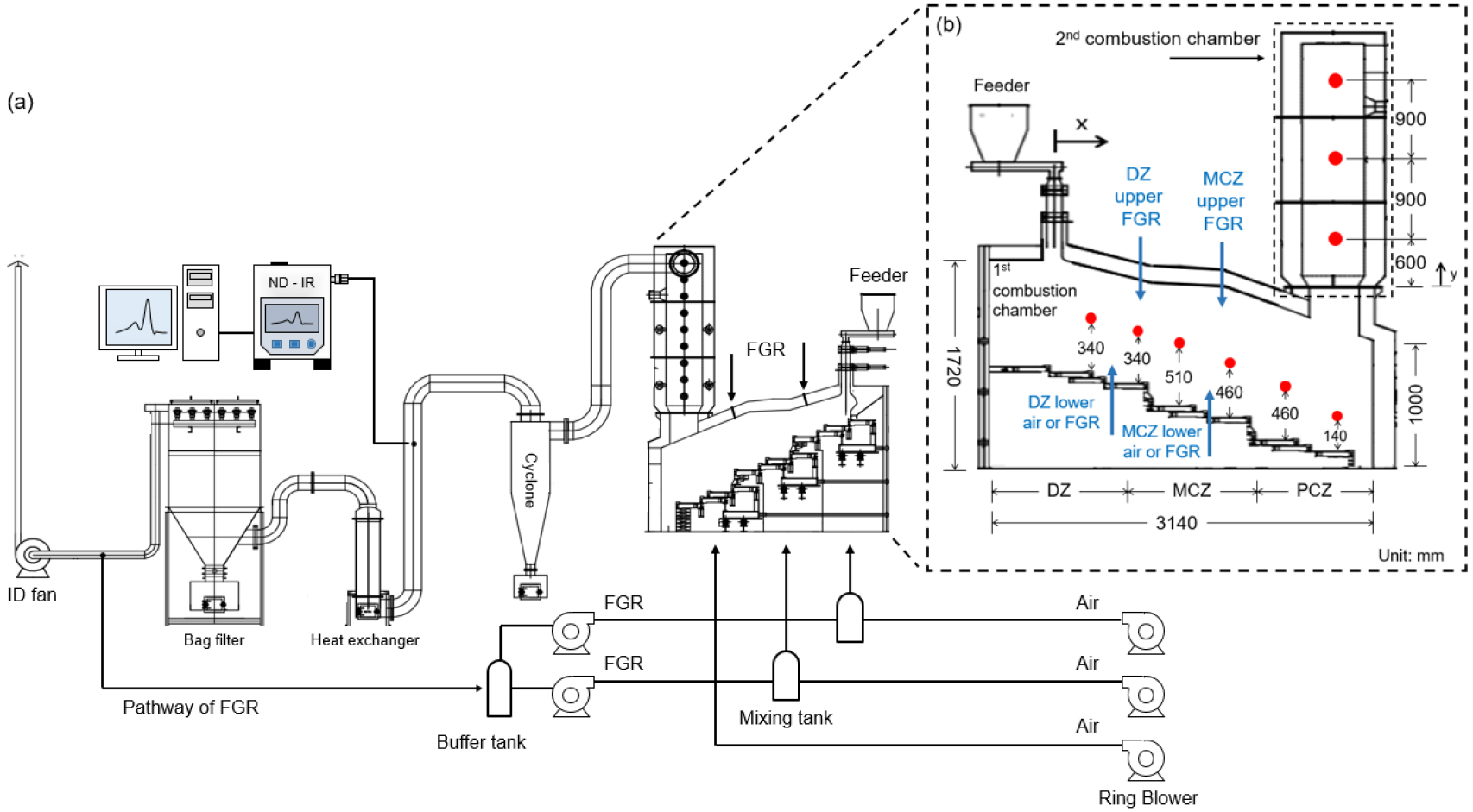
- As waste management practices and policies have evolved, the composition of municipal waste has shifted, raising its average heating value from 1,945 …
- As waste management practices and policies have evolved, the composition of municipal waste has shifted, raising its average heating value from 1,945 kcal/kg to 4,025 kcal/kg over the past 20 years. This increase has resulted in incineration conditions that exceed the design specifications of existing facilities, with a notable rise in the combustion rate due to higher fractions of volatile synthetic resins. Consequently, instead of achieving uniform combustion as initially designed, the process now completes much faster, creating localized high-temperature zones. These zones cause issues such as facility damage, clinker formation, elevated NOx emissions, and reduced operational efficiency. To address these challenges, this study applies the MILD (moderate and intense low oxygen dilution) combustion technique using FGR (flue gas recirculation) technology in a 180 kWth stoker-type incinerator. Wall temperatures were measured with nine thermocouples, exhaust gas concentrations were analyzed with a non-dispersive infrared (ND-IR) gas analyzer. The experiments varied FGR ratios (0%, 50%, 100%) and FGR injection locations to identify optimal operating conditions. The results showed that increasing the FGR ratio significantly reduced the maximum temperature within the incinerator. The greatest temperature reduction, along with decreased CO and NO emissions, was observed when 100% FGR was injected into both the upper and lower high-temperature zones. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study of MILD Combustion Characteristics Using FGR in a 180 kWth Incinerator
-
Research Article
-
Explosion Characteristics of Hydrogen(Ammonia) Fuel with Various Cracking Ratios for Power Generation
크래킹 비율에 따른 발전용 수소(암모니아) 연료의 폭발특성
-
Mingyu Kim, Inho Kim, Keeman Lee
김민규, 김인호, 이기만
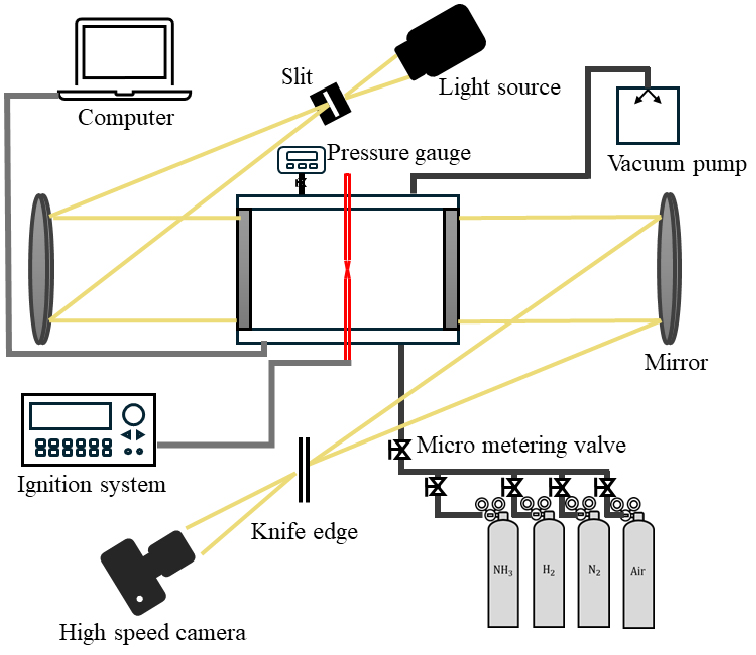
- Ammonia is being explored as a carbon-free fuel; however, its narrow flammability limits, low laminar burning velocity, and high ignition energy make …
- Ammonia is being explored as a carbon-free fuel; however, its narrow flammability limits, low laminar burning velocity, and high ignition energy make it difficult to use as a commercial fuel. To overcome these limitations, the addition of hydrogen has been widely investigated. In this study, the explosion characteristics of ammonia cracking fuel were experimentally examined in a cylindrical constant-volume combustion chamber, with the ammonia cracking ratio and equivalence ratio as key variables, and the results were compared with corresponding heat loss behavior. As the cracking ratio increased, the maximum explosion pressure (Pmax) and index (KG) increased, while the explosion duration (tc) and heat loss (qtr) decreased. With respect to the equivalence ratio, both the maximum explosion pressure and index increased under lean conditions up to Φ = 1.1 and then decreased under rich conditions. Schlieren imaging of the flame reaction zone revealed that buoyancy instability dominated at a cracking ratio of 7%, hydrodynamic instability at 16%, and thermo-diffusive instability at 62%. The thermo-diffusive instability was found to enhance the explosion characteristics. - COLLAPSE
-
Explosion Characteristics of Hydrogen(Ammonia) Fuel with Various Cracking Ratios for Power Generation
-
Research Article
-
Effect of Swirl Structure on Flame Stability in Pulverized-Coal Ammonia Co-Firing and Ammonia Sole-Firing under Load Variation
미분탄-암모니아 혼소 및 암모니아 전소 부하 변화 시 스월 구조에 따른 화염 안정성 평가
-
Jinheon Choi, Tae-Young Mun, Jaewon Chung, Hookyung Lee
최진헌, 문태영, 정재원, 이후경
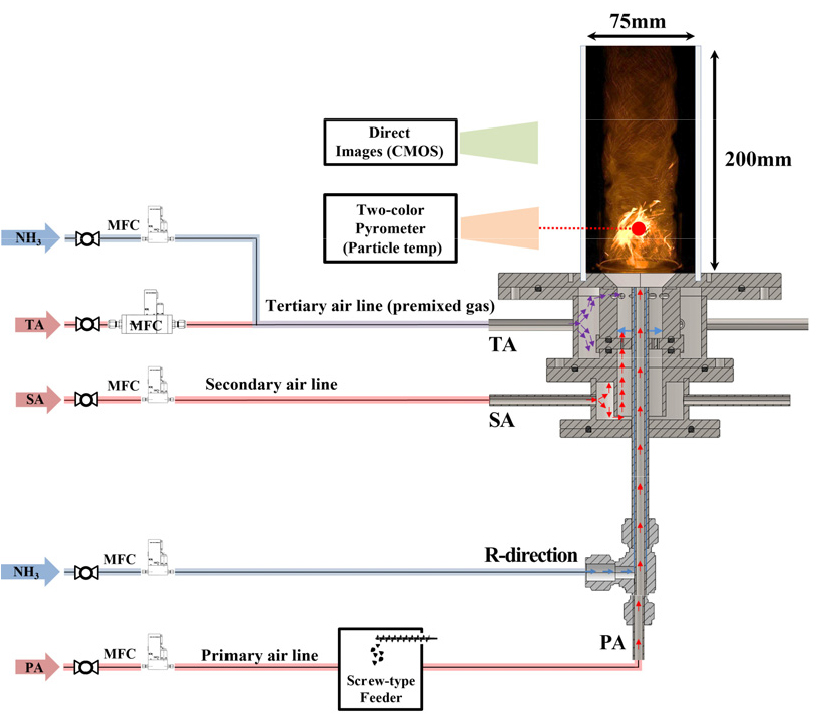
- Ammonia-coal co-firing can reduce CO2 emissions in pulverized-coal boilers, but ammonia’s low burning velocity makes flame stabilization a key design issue. …
- Ammonia-coal co-firing can reduce CO2 emissions in pulverized-coal boilers, but ammonia’s low burning velocity makes flame stabilization a key design issue. This study investigates the impact of swirler geometry on flame stability in a lab-scale pulverized coal-ammonia burner. Six tangential swirlers, combining three port numbers (8, 6, 4) and two axial positions (upper: U, lower: D), were tested over 1-5 kWth. Flame imaging and two-color pyrometry quantified apparent flame intensity and coal particle temperature, and non-reacting CFD clarified the internal recirculation and turbulence fields. The 8-port cases (U-8, D-8) secured the widest stable operating range, whereas 4-port swirlers exhibited frequent ignition failure and blow-off at low loads. D-type geometries enhanced stability by promoting recirculation of coal reaction heat into the flame root. These results provide practical design guidelines for stabilizing ammonia-coal co-firing burners. - COLLAPSE
-
Effect of Swirl Structure on Flame Stability in Pulverized-Coal Ammonia Co-Firing and Ammonia Sole-Firing under Load Variation
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Society of Combustion
Journal of the Korean Society of Combustion
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Society of Combustion
Journal of the Korean Society of Combustion











