-
Research Article
-
Study on Zero-Carbon Ammonia Staged Combustion
무탄소 암모니아 다단연소 특성 연구
-
Eun-Seong Cho, Yuin Jin, Moonsoo Cho, Hyunwook Jegal, Minjung Pyo
조은성, 진유인, 조문수, 제갈현욱, 표민중
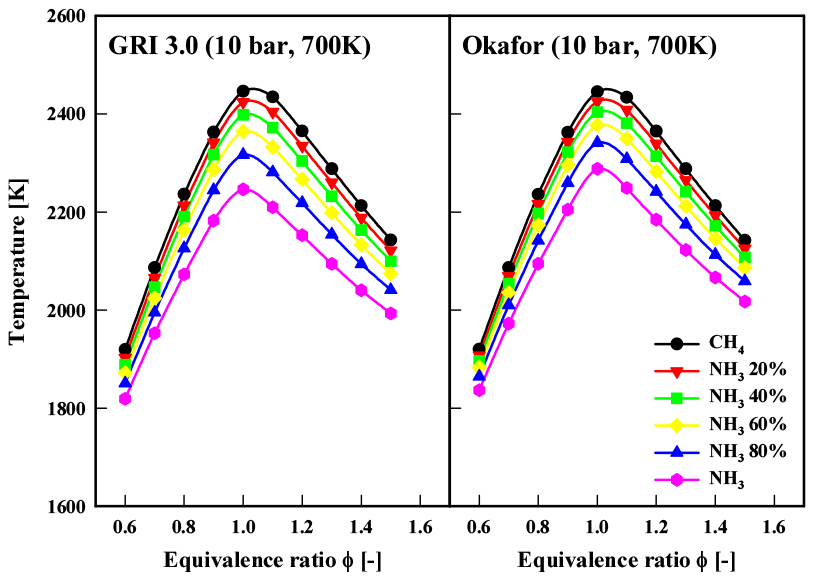
- This study explores the staged combustion characteristics of ammonia(NH3), a zero-carbon fuel and hydrogen carrier, in comparison with methane(CH4 …
- This study explores the staged combustion characteristics of ammonia(NH3), a zero-carbon fuel and hydrogen carrier, in comparison with methane(CH4), using numerical simulations conducted with the ANSYS CHEMKIN-Pro reactor network model. Ammonia fuel requires effective strategies to mitigate nitrogen oxide(NOx) emissions. The study investigates four combustor configurations, each featuring different primary and secondary zone designs, to assess the effectiveness of staged combustion—combining rich premixed and air-diluted stages—in reducing fuel NOx formation. Key parameters such as primary zone equivalence ratio, operating pressure, co-firing effects, and residence time(linked to primary zone length) are analyzed. The results show that residence time in the primary zone plays a critical role in governing NOx emissions. While methane combustion primarily generates thermal NOx, ammonia combustion leads to the formation of fuel NOx, with co-firing scenarios exhibiting intermediate emissions. The findings highlight the potential of optimizing staged combustion configurations and primary zone parameters to significantly reduce NOx emissions, advancing ammonia’s viability as a sustainable fuel. These insights provide essential guidelines for the design of efficient, low-emission ammonia-based combustion systems. - COLLAPSE
-
Study on Zero-Carbon Ammonia Staged Combustion
-
Research Article
-
The Effect of Electric Field on Thermo-Acoustic Instability in a Laminar Premixed Flame
전기장 인가에 따른 층류 예혼합 화염의 열-음향 불안정성 변화
-
Taehun Kim, Hyemin Kim
김태훈, 김혜민
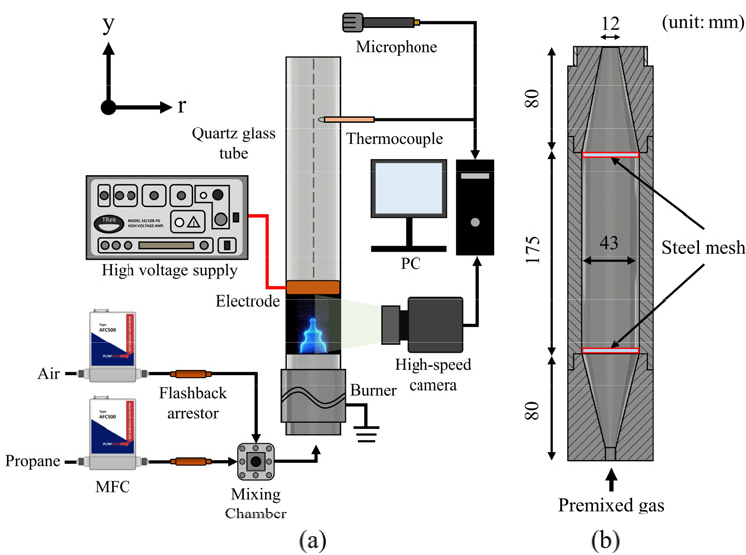
- In this study, the effect of an electric field on thermo-acoustic instability in a laminar premixed flame was investigated. Flame surface fluctuations …
- In this study, the effect of an electric field on thermo-acoustic instability in a laminar premixed flame was investigated. Flame surface fluctuations and sound pressure were measured using a high-speed camera and a microphone. The results showed that the flame surface oscillated under the no-voltage condition, with these oscillations intensifying under –3 kV and decreasing under +3 kV. This behavior remained consistent even as the inlet velocity increased. In the frequency domain, applying –3 kV shifted the dominant frequency to a higher range, whereas no distinct peak was observed under the +3 kV condition. Regarding the sound pressure level, –3 kV had little impact, whereas +3 kV reduced it by up to 23.8% under stoichiometric conditions. Furthermore, this effect remained effective even under lean premixed conditions. - COLLAPSE
-
The Effect of Electric Field on Thermo-Acoustic Instability in a Laminar Premixed Flame
-
Research Article
-
Acoustic Prediction and Analysis of Full-scale Can-annular Combustors Using Cross-talk Acoustic Boundary Condition
Cross-talk 음향 경계조건을 이용한 실스케일 Can-annular 연소기의 음향 특성 예측 및 분석
-
Junwoo Jung, Myunggon Yoon, Daesik Kim
정준우, 윤명곤, 김대식
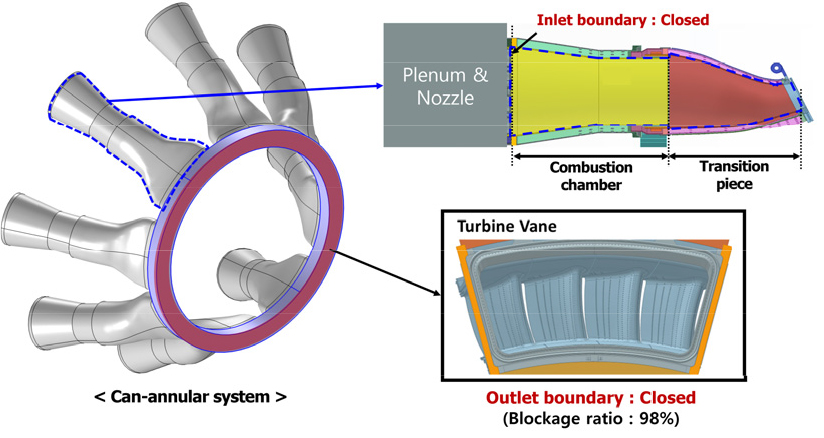
- Can-annular combustor systems exhibit unique thermoacoustic characteristics due to cross-talk coupling effects between individual cans. This study investigates these characteristics and validates …
- Can-annular combustor systems exhibit unique thermoacoustic characteristics due to cross-talk coupling effects between individual cans. This study investigates these characteristics and validates the use of cross-talk acoustic boundary conditions for predicting system behavior through single-can analysis within a full-scale can-annular combustor system. A three-dimensional acoustic analysis was performed using a Helmholtz solver, and cross-talk boundary conditions derived from one-dimensional modeling were applied to the single-can configuration. The results demonstrate that single-can analysis incorporating cross-talk boundary conditions can accurately reproduce key system-level features, including mode clustering. This validated approach enables effective system prediction using single-can testing, thereby reducing the reliance on full-system experiments. However, limitations remain in the high-frequency range, where resonant modes associated with the transition piece geometry are not fully captured. - COLLAPSE
-
Acoustic Prediction and Analysis of Full-scale Can-annular Combustors Using Cross-talk Acoustic Boundary Condition
-
Research Article
-
Analysis of Combustion Instability Characteristics of a Single-Nozzle Combustor in a Natural Gas-Hydrogen Co-firing Gas Turbine under Varying Operating Pressures
압력 변화에 따른 천연가스-수소 혼소 가스터빈 싱글 노즐 연소기의 연소불안정 특성 분석
-
Junwoo Jung, Daesik Kim, Min Kuk Kim, Jeongjae Hwang, Won June Lee
정준우, 김대식, 김민국, 황정재, 이원준
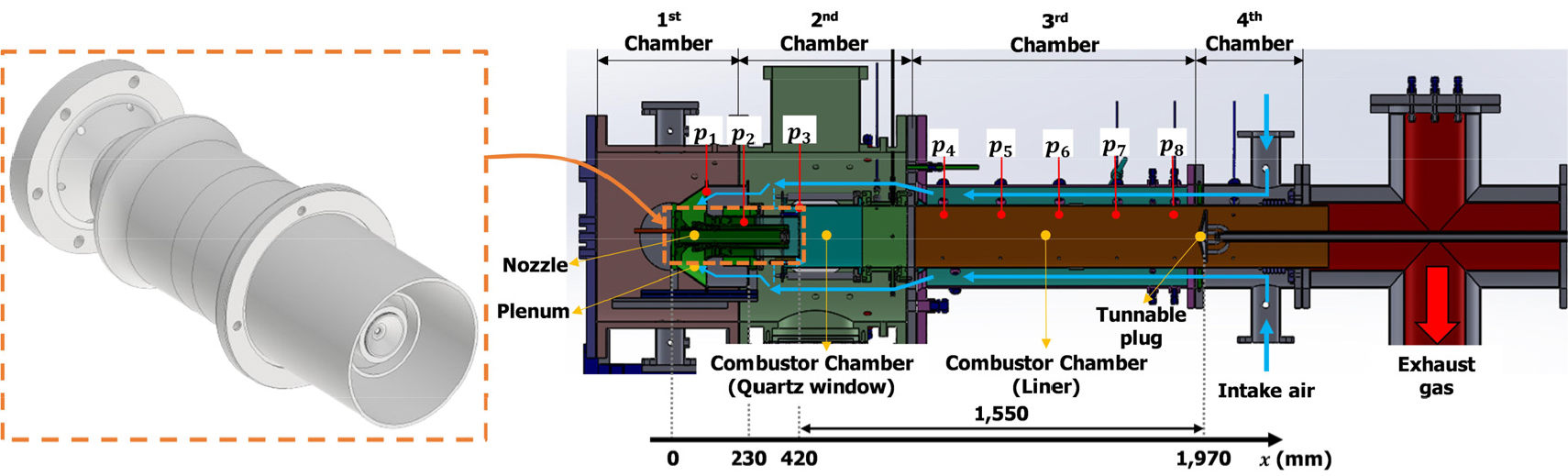
- This study analyzes combustion instability characteristics in a natural gas-hydrogen co-firing gas turbine single-nozzle combustor under varying pressure conditions. Experiments were conducted …
- This study analyzes combustion instability characteristics in a natural gas-hydrogen co-firing gas turbine single-nozzle combustor under varying pressure conditions. Experiments were conducted with hydrogen co-firing ratios of 0% and 30% at pressures from 1.3 to 3.0 bar, combined with OH* chemiluminescence imaging and 1D thermoacoustic analysis. Results show that both hydrogen co-firing and pressure increases reduce flame length, thereby decreasing time delay in the flame transfer function and increasing combustion instability susceptibility. 1D thermoacoustic analysis revealed that pressure effects occur through flame dynamics variations rather than acoustic mechanisms. Gain margin analysis demonstrates that the combined effects of hydrogen co-firing and pressure increases substantially reduce the stable operating envelope for this combustor configuration. - COLLAPSE
-
Analysis of Combustion Instability Characteristics of a Single-Nozzle Combustor in a Natural Gas-Hydrogen Co-firing Gas Turbine under Varying Operating Pressures
-
Research Article
-
Experimental Study for Development of Endothermic Decomposition Model of Supercritical n-Dodecane
초임계 n-dodecane의 흡열분해 화학반응 모델 개발을 위한 실험적 연구
-
Seung Mook Park, Seung Hyeon Lee, Jun Su Kang, Hyung Ju Lee
박승묵, 이승현, 강준수, 이형주
- The pyrolysis characteristics of hydrocarbon aviation fuel have a significant impact on the cooling performance of active regenerative cooling systems for hypersonic …
- The pyrolysis characteristics of hydrocarbon aviation fuel have a significant impact on the cooling performance of active regenerative cooling systems for hypersonic vehicles and the combustion performance of scramjet engines. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the thermal cracking characteristics of n-dodecane, the main component of hydrocarbon jet fuel, using a batch reactor experimental setup. In particular, since fuel in actual regenerative cooling channels reaches a supercritical state, experiments were conducted to allow pyrolysis at pressures of 4 MPa, temperatures ranging from 500 to 600°C, and reaction times between 100 and 220 seconds. Under these reaction conditions, the maximum fuel conversion and gas production rates were found to be approximately 80% and 42%, respectively. Furthermore, based on the experimental results, the distribution of gas and liquid products according to fuel conversion was quantitatively analyzed, and a global one-step reaction PPD(Proportional Product Distribution) model for n-dodecane was developed. - COLLAPSE
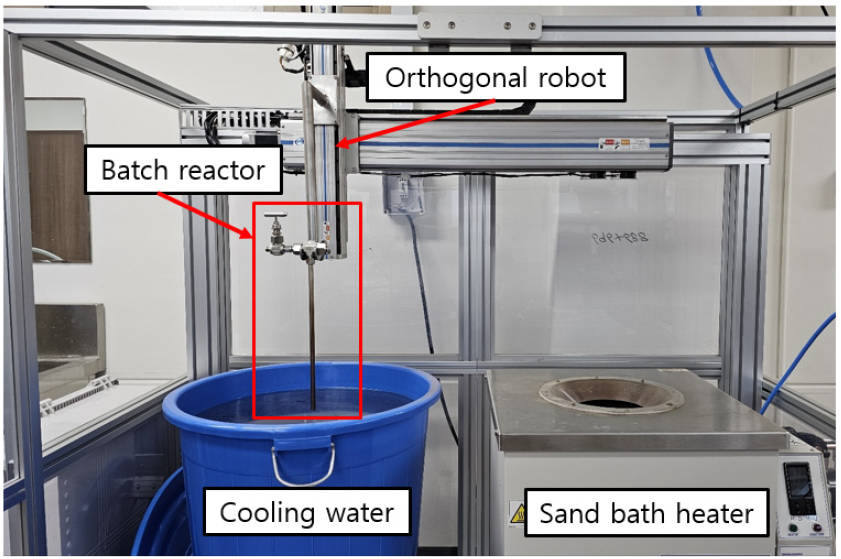
-
Experimental Study for Development of Endothermic Decomposition Model of Supercritical n-Dodecane
-
Research Article
-
Hydrogen Co-Firing Characteristics of a Gas Turbine Combustor with Axial Fuel Staging Combustion
축방향 다단연소가 적용된 가스터빈 연소기의 수소 혼소 특성
-
Jeongjae Hwang, Won June Lee, Kyungwook Min, Jaehyun Kim, Do Won Kang, Ju Hyeong Cho, Han-Seok Kim, Min Kuk Kim
황정재, 이원준, 민경욱, 김재현, 강도원, 조주형, 김한석, 김민국
- A can-type gas turbine combustor with axial fuel staging (AFS) was developed to investigate combustion characteristics under natural gas and hydrogen co-firing. …
- A can-type gas turbine combustor with axial fuel staging (AFS) was developed to investigate combustion characteristics under natural gas and hydrogen co-firing. Experiments evaluated the effects of AFS fuel split and hydrogen content on emissions and stability. NOx emissions were minimized at an AFS split of ~16% across all hydrogen levels, while increasing hydrogen content slightly raised NOx and significantly reduced CO emissions. Higher AFS splits enhanced jet penetration, as shown by changes in the exit temperature profile. Combustion dynamics amplitude decreased at specific hydrogen contents, indicating the potential of AFS for stabilizing hydrogen co-firing. - COLLAPSE
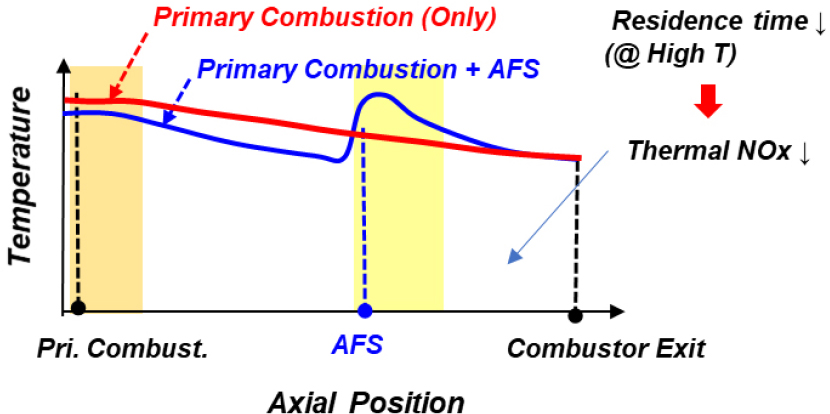
-
Hydrogen Co-Firing Characteristics of a Gas Turbine Combustor with Axial Fuel Staging Combustion
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Society of Combustion
Journal of the Korean Society of Combustion
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Society of Combustion
Journal of the Korean Society of Combustion











